What is CNC?
Terminology, history and applicable materials
By definition CNC (Computerized Numerical Control) means controlling a machine tool or other device automatically by a computer instead of direct manipulation by an operator. Machine tools, on the other hand, use different processes like milling or turning for a piece of raw material to produce a ready workpiece – this is often called discrete manufacturing. It’s notable that the first NC-machines in 1940s and 1950s used paper tape or punched cards to control the motion. ‘NC’ turned ‘CNC’ only after computers were introduced as controllers in the 1960s. The programming language that turns an NC-program – information – into precise machine tool movements is called G-code.

Modern 5-axis milling machine making a cogwheel
At first, most of of the CNC machines were custom-built for a certain part manufacturing needs, like in the below picture, although general purpose machinery were also produced for turning or drilling processes for example. Since the 1990s general purpose CNC machining centers, suitable for certain processes and part diameters (e.g. 4-axis milling machine with a table of 800x800mm) have evolved tremendously and taken over majority of the markets.

To give some contrast, here’s a special-purpose horizontal CNC milling + drilling machine from 1970s used in engine block manufacturing.
In principle CNC machines can be used on any material from metal to composites, wood, plastics and so on. Although Fastems has worked with customers in all of mentioned material domains, this page is focused on metals and composites.
The main CNC machining processes
CNC as such can be applied in a huge variety of manufacturing processes and machinery. In this page we focus on machining operations that can be identified by their production of chips. This means the processes are substractive by nature and the equipment involved are oftentimes called cutting machine tools.
Referring to the page title, CNC machining can be defined as automatically and digitally controlled machining processes. Main machining processes include:
- Milling, where the spindle rotates removing material.
- Turning, where the cylindrical workpiece rotates while spindle is fixed removing the material
- Drilling, where a hole is cut into the workpiece
- Grinding, where a rolling, abrasive wheel removes light amounts of material
- Sawing where material is cut (into parts) with a blade.
- Finishing operations
- Filing that is about light amounts of material removing, combining grinding and sawing and is used mostly in deburring
- Polishing and brushing, where a smooth or shiny surface is created with abrasive process.
The above are often called as conventional machining and abrasive processes. There are many other operations such as EDM (electrical discharge machining) or laser or water-jet cutting within the category of material removing operations that are not discussed in this page. Sometimes machining operations are also combined with additive manufacturing processes in hybrid machines. For more information on material removing processes, see for example Mikell Groover’s Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing where the below illustration is from:
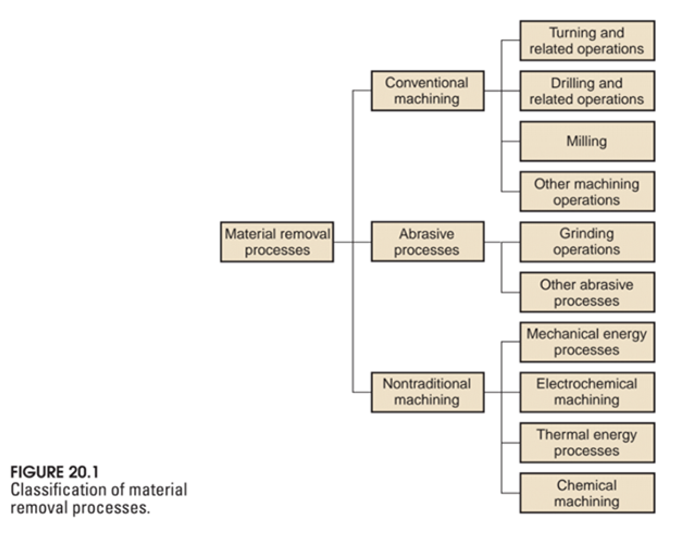
The main types of CNC machines
Given the machining operations context set above, the most typical CNC machine tools are:
- 3-, 4- and 5-axis milling machines, sometimes also called machining centers
- Turning machines
- Multitasking machines: turn-mills and mill-turns that combine a milling spindle and workholding for turning operations.
- Grinding and sawing machines

This lathe can also perform milling operations
When discussing the finishing and other supportive processes for machining, one can also add to the list various machinery or cells that are digitally and automatically controlled via PLC (programmable logic controller) such as deburring with a robot or can be considered to be CNC machines such as a marking machine.
These can include:
- Deburring with robot
- Sanding with robot
- Polishing with robot
- Washing machines
- Marking machines
- Measuring machines

Deburring with a robot
CNC machining automation
Automating your CNC machines is a vast topic. This section begins the journey by explaining the typical activities offering automation potential. Finally, an illustration combining the type of automation with machinery/process types is introduce summarizing this whole page.
What activities can you automate?
Automation simply means the reduction of human intervention to a process. Below you can see the two main categories of activities offering the most automation potential around CNC machines. The best practices on how automate them are discussed here
Automated production scheduling in CNC automation system
Automating production planning and resource management
Orchestrating your people, machinery and IT-systems to work as one. In practice this means features like:
- Automated information flows between different data systems and machinery or cells.
- Proactively and constantly updating production plan based on production orders and their priorities
- Automatic fetching of orders from ERP
- Operator guidance to always take the right action at the right time
- Workpiece manufacturing ‘recipe’ handling
- Managing of (complex) production phasing within production process
- Proactive resource management vs production plan and reports of missing resources.
- Fixtures, pallets and grippers
- Raw materials
- NC-programs
- Cutting tools, tool data and off-sets
- Reporting and analytics
- Production and machinery KPIs such as utilization, OEE, availability…
- Order progress views
- Inventory / work-in-progress
- Production event history and traceability
- Automated documentation (paperless production)

Robots can be utilized to deliver zero-point plates to the machine table.
Automating physical movement and operations
Automation hardware can replicate reproducible and stable processes with very high efficiency and accuracy. In practice this can mean activities like:
- Transfers of (zero-point) machining pallets to/from machine table.
- Automated fixture loading/unloading with a robot
- Direct transferring of workpieces to machine table or chuck
- Automated chuck adjustments or changes
- Gripper and tool changes in robots
- Tool transfers to tool magazines
- Workpiece movements to/from machining supportive processes like
- Deburring
- Washing
- Heat treatment
- Washing
- Marking
- Polishing
- Measuring
- Raw material management and transfers
- Semi-finished product management and transfers
